



Accelerating your AI Success
ExploremedDARE stands for ‘Medical Data Resources’ which corresponds to our dedication to deliver diverse, secured and high-quality medical data and its curation.
Being on the market since 2020, our highly-motivated team of professionals gained extensive experience on driving AI projects of various complexity. This was done thanks to building up a solid network of hospital sites in the US and Europe and cooperating with professional doctors of different specialties. By now we successfully work with clients which are both startups and Fortune 500 companies.
We are excited to be at the forefront of developing cutting edge technology with our clients. Accelerating your AI success, together we accelerate a healthier future.
years on the market
patient studies
projects in data collection and data curation
hours of data curation projects
clients (including multiple Fortune500 members)
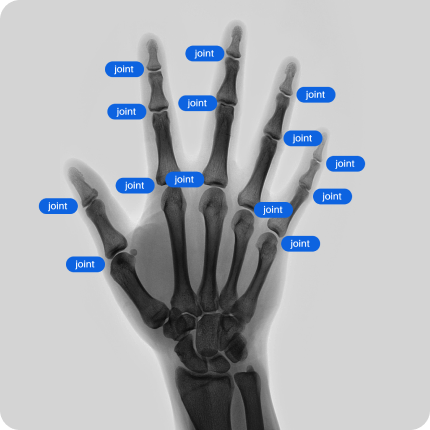
Our network of providers of healthcare data have access to CT, MRI, X-Ray scans of various body parts and pathologies. We provide both retrospective data and can collect data according to your technical requirements.
We have equipment and a trained team to collect video data from hospital sites. This includes videos in operating rooms and of various surgeries. Videos can be adjusted to clients’ requirements.
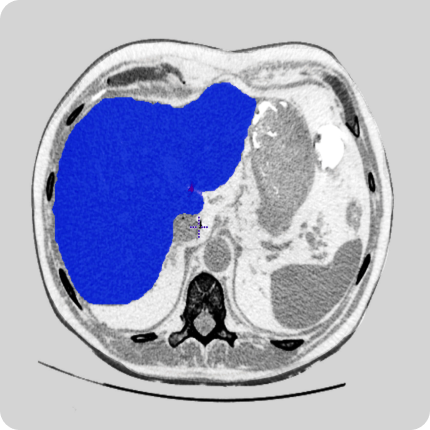
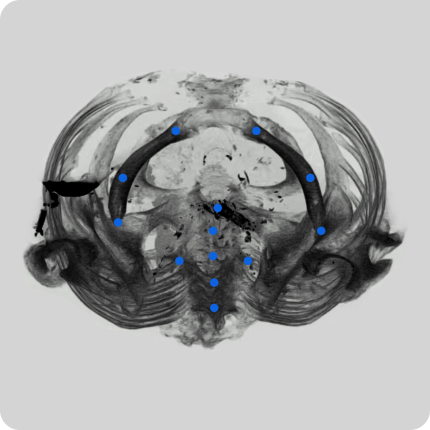
Our team of radiologists has delivered multiple data curation projects to our clients. These services include labeling, contouring, 2D and 3D modeling, and quality assurance. We work with open-sourced tools and tools of our clients.

To stay in compliance with the regulatory standards set forth by European and US authorities, our data is properly anonymized and checked by our in-house team of quality assurance. We are using both commercial and our own software to anonymize the data of our providers.

Our experience in developing AI projects from scratch has given us many opportunities to deliver other services to our clients like project audit, database creation from scratch, developing instructions for data curation projects, and many more.
medDARE datasets are always fully anonymized and are securely stored on EU-based servers. All storage and transfer to clients is done in full compliance with GDPR and HIPAA regulations.



